LIFE CYCLE
ALUMINUM CAN PROCESS

Aluminum cans are 100% recyclable
Aluminum cans are not only convenient but also great environmental warriors! Learn about the life cycle of aluminum cans, see how they are recycled, and do your part for environmental protection!

Finished Can
Recycled Cans
Compacted Aluminum

Crushing

Remelting
Aluminum Ingot
Aluminum Coil
Finished Can
Aluminum recycling is an important strategy for sustainable development, providing innovative solutions to protect the earth’s resources. Producing new aluminum from waste aluminum requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce primary aluminum, demonstrating the impressive effectiveness of resource recycling. Through recycling, we can significantly reduce the energy needed for bauxite mining and primary smelting, effectively lowering the material’s carbon footprint. “Closed-loop recycling” is the most efficient way to maximize resource utilization, and aluminum beverage cans are a perfect example of this concept.
Description
Aluminum beverage cans are one of the most recycled packaging materials in the world, with a consistently high recycling rate. The recycled aluminum can be used to make aluminum plates for new beverage cans and has a wide range of other applications, showcasing its excellent recycling characteristics.

Recycled Cans
The trimmings(offcuts) generated during the production of aluminum cans are a resource that cannot be ignored in the manufacturing process. Our specialized factory is equipped with dedicated conveyor belts and precise collection equipment, which efficiently and promptly separate these aluminum scraps from the production line. This precise recycling mechanism ensures maximum resource utilization and reflects the sustainable philosophy of the production process.
Process
1. Collection: The factory collects aluminum scraps from various sources, including waste materials generated during the production process, sample cans from trial production, and defective products, etc., to ensure that no resources are wasted.
2. Transportation: The collected aluminum materials are transported to the recycling area of the plant for subsequent processing.
2. Transportation: The collected aluminum materials are transported to the recycling area of the plant for subsequent processing.
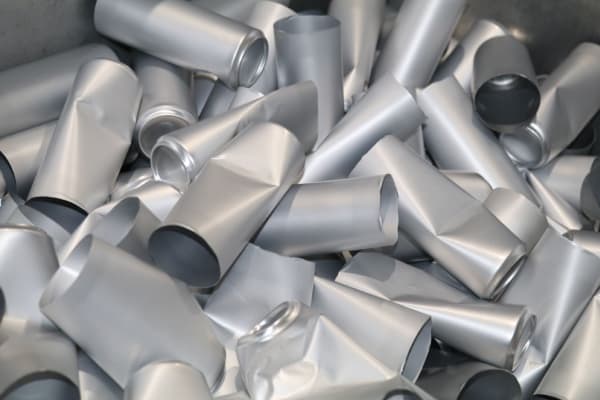

Compacted Aluminum
In the aluminum can recycling process, compressing the large volume of aluminum material is a crucial step. Proper handling not only greatly reduces the volume but also improves transportation and storage efficiency and enhances the subsequent melting process.
Process
1. Compression: To reduce volume, the aluminum material is compressed into high-density aluminum blocks (Compacted aluminum) for easier subsequent transportation and handling.
2. Storage: The compressed aluminum blocks are properly stored in a dry warehouse to prevent moisture or contamination and to ensure the quality of the material.
2. Storage: The compressed aluminum blocks are properly stored in a dry warehouse to prevent moisture or contamination and to ensure the quality of the material.
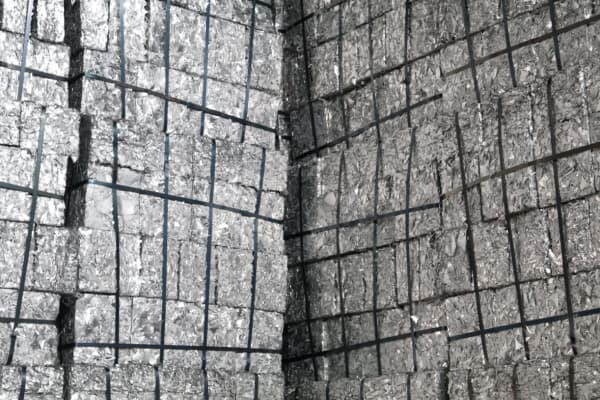

Crushing
After the compacted aluminum arrives at the recycling plant, it is typically handled by cranes or forklifts. Once unloaded, the compacted aluminum is neatly stacked for further processing. The recycling plant then crushes it into smaller particles and processes it through several stages, including screening, magnetic separation, air separation, and manual sorting, to thoroughly remove various impurities. This ensures that the final product meets the purity requirements for the refining process.
Process
1. Crushing: Crushing the aluminum briquettes into smaller particles to facilitate screening and subsequent melting operations.
2. Screening: Classifying the crushed aluminum material according to particle size to facilitate subsequent classification and treatment.
3. Magnetic Separation: Removing ferromagnetic impurities mixed in the aluminum material, such as iron nails, iron wire, and other metals.
4. Wind Sorting: Removing lighter impurities in the aluminum materials, such as plastic, paper scraps, and other non-metallic materials.
5. Hand-selecting: Manually picking out impurities that are difficult to separate mechanically, such as rubber, leather, and other special materials.
2. Screening: Classifying the crushed aluminum material according to particle size to facilitate subsequent classification and treatment.
3. Magnetic Separation: Removing ferromagnetic impurities mixed in the aluminum material, such as iron nails, iron wire, and other metals.
4. Wind Sorting: Removing lighter impurities in the aluminum materials, such as plastic, paper scraps, and other non-metallic materials.
5. Hand-selecting: Manually picking out impurities that are difficult to separate mechanically, such as rubber, leather, and other special materials.
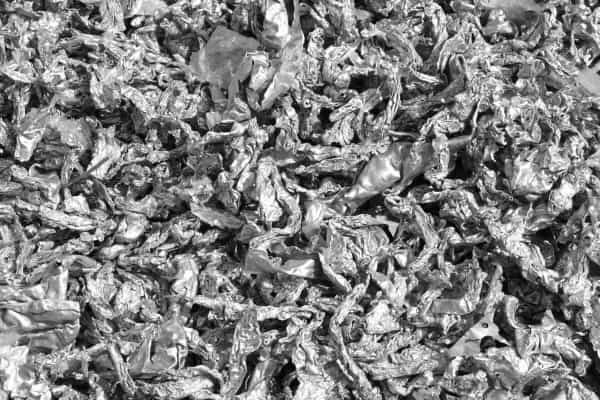

Remelting
The smelting process for aluminum can recycling is a critical step in converting recycled aluminum cans into reusable aluminum liquid. This process is not only efficient but also environmentally friendly, as recycling aluminum requires much less energy than extracting it from bauxite.
Process
1. Pouring: Pure aluminum liquid is poured into the mold to make aluminum ingot or other desired shapes.
2. Demolding: Remove the aluminum ingot from the mold after it has completely cooled down and solidified.
3. Inspection: The finished ingot is inspected to ensure that it meets the established quality standards.
2. Demolding: Remove the aluminum ingot from the mold after it has completely cooled down and solidified.
3. Inspection: The finished ingot is inspected to ensure that it meets the established quality standards.
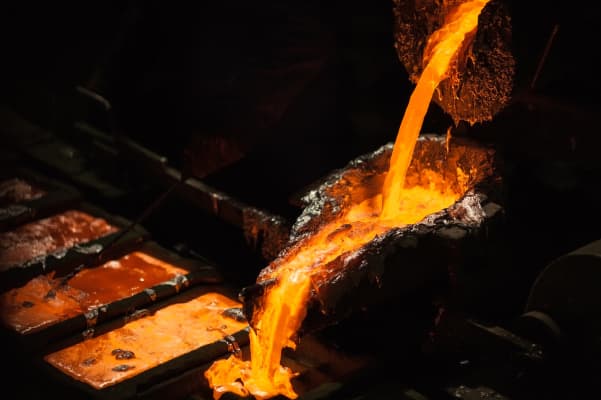

Aluminum Ingot
After melting the recycled aluminum cans into liquid aluminum, the next step is to pour these high-purity liquid aluminum into aluminum ingots for subsequent processing and utilization.
Process
1. Pouring: Pure aluminum liquid is poured into the molds to make aluminum ingots or other desired shapes.
2. Demolding: Remove the aluminum ingot from the mold after it has cooled down and solidified.
3. Inspection: The finished ingot is inspected to ensure that it meets the established quality standards.
2. Demolding: Remove the aluminum ingot from the mold after it has cooled down and solidified.
3. Inspection: The finished ingot is inspected to ensure that it meets the established quality standards.
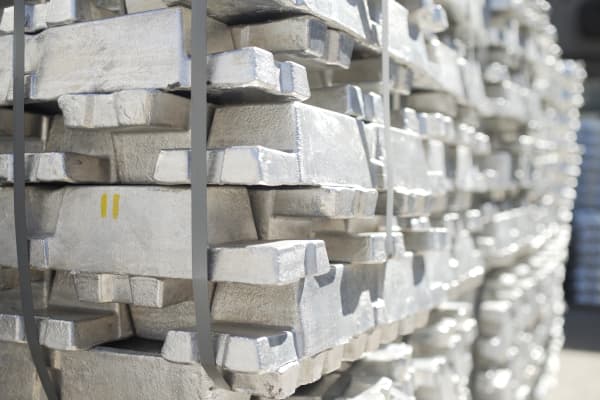

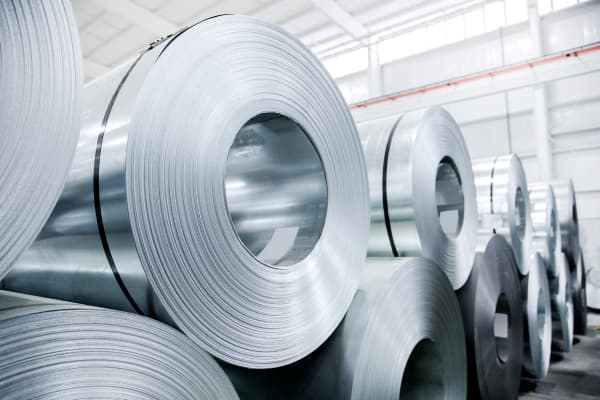
Aluminum Coil
The process from recycled aluminum cans to aluminum coils involves several complex steps, including hot rolling, cold rolling, and quality inspection, to produce high-quality material that meets the requirements.
Process
1. Hot rolling: The heated aluminum ingot is fed into the hot rolling mill, where its thickness is reduced through high temperature and high pressure, and it is given a specific width.
2. Cold Rolling: The aluminum plate from hot rolling undergoes cold rolling to improve strength, hardness, and surface finish. Intermediate annealing is required between cold rolling steps to restore the plate’s workability and prevent cracks.
3. Heat treatment: Some alloys require aging treatment to enhance their strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance.
4. Quality Inspection: The produced aluminum coils undergo strict quality inspections to ensure they meet the relevant standards.
2. Cold Rolling: The aluminum plate from hot rolling undergoes cold rolling to improve strength, hardness, and surface finish. Intermediate annealing is required between cold rolling steps to restore the plate’s workability and prevent cracks.
3. Heat treatment: Some alloys require aging treatment to enhance their strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance.
4. Quality Inspection: The produced aluminum coils undergo strict quality inspections to ensure they meet the relevant standards.

GREAT CHINA METAL
Aluminum is one of the few natural resources on Earth that
can be
recycled indefinitely.
100% recyclable, aluminum can be endlessly recycled into new cans. In the U.S., it takes only 60 days for a used aluminum can to go through the recycling pipeline, be turned into a new can, and be back on the retail shelf for sale.
Beverage Cans



STEP1
Rinse
Rinse inside and out with clean water.
STEP2
Dry
Turn the can upside down to drain any remaining water.
STEP3
Flatten the Can
Compress the can to save storage space.
STEP4
Metal Recycling
Place in designated recycling bins.
Food Cans



STEP1
Rinse
Rinse inside and out with clean water.
STEP2
Drying
Turn the can upside down to drain any remaining water.
STEP3
Sorting & Recycling
Food cans often have plastic lids—be sure to remove and sort them properly!

Recovery Value / Resource Recyclability
The Recycling Value of Aluminum Cans is Much Higher Than Their Recycling Cost
The total economic benefit derived from recycling a used aluminum can far exceeds the actual cost paid to recyclers and the total cost of remanufacturing a new can. In terms of recycling benefits, this is unparalleled by other packaging materials such as PET bottles and glass bottles!
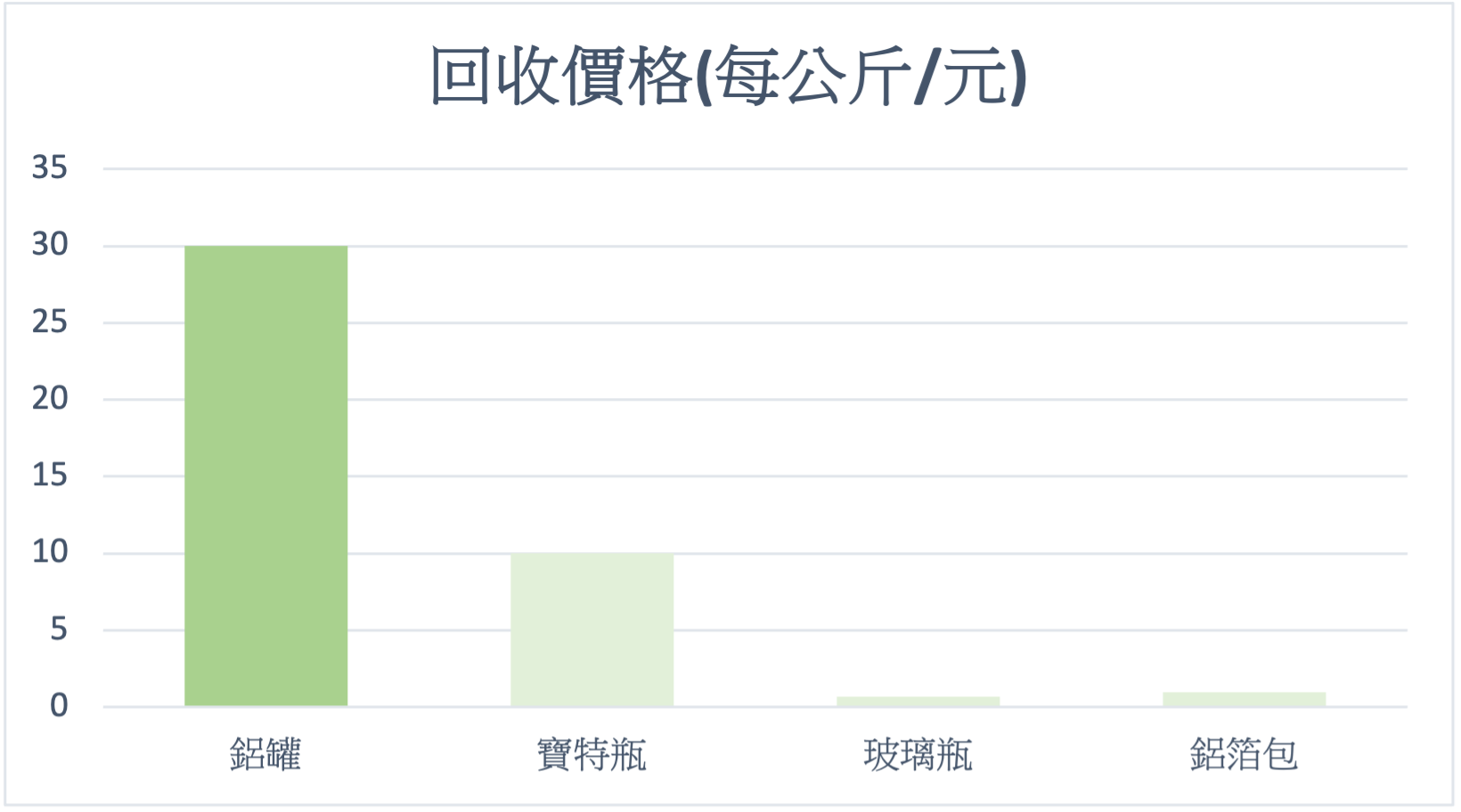
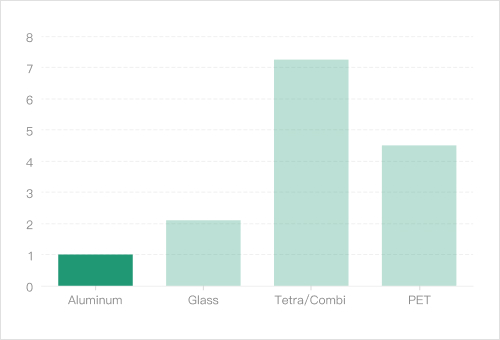
Benefits of Recycling Aluminum Cans
Recycling aluminum cans helps save energy, reduce emissions, minimize resource waste, lower carbon footprint, and promote aluminum material reuse.
Energy Saving
Recycling aluminum cans requires only 5% of the energy needed to refine aluminum from bauxite ore.
- The energy saved by recycling one aluminum can is enough to power a TV for 3 hours or a 100-watt incandescent bulb for 4 hours, while reducing air pollution by 95%.
- Recycling 40 aluminum cans saves the equivalent energy of one gallon of oil.

Protecting the Earth and the Environment
Aluminum cans can be infinitely recycled in a closed-loop system.
- Using recycled aluminum reduces greenhouse gas emissions by 95% and requires minimal energy.
- Recycling aluminum helps protect the environment and supports sustainable resource use.
